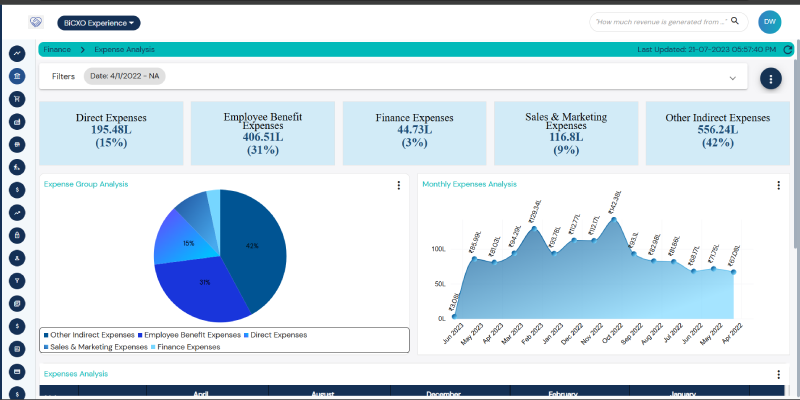
What is an expense data analysis?
The process of reviewing financial expenses is known as expense data analysis. It entails classifying, monitoring and assessing business operations expenses. The goal is to learn more about spending trends. Budgeting, financial decision-making and cost control are all aided by expense data analysis. To make sure that financial resources are distributed effectively, businesses employ expense data analysis. It is crucial to preserving long-term sustainability and profitability. Expense data analysis is a tool used by organizations to track expenditures and find areas where excessive spending can be cut.
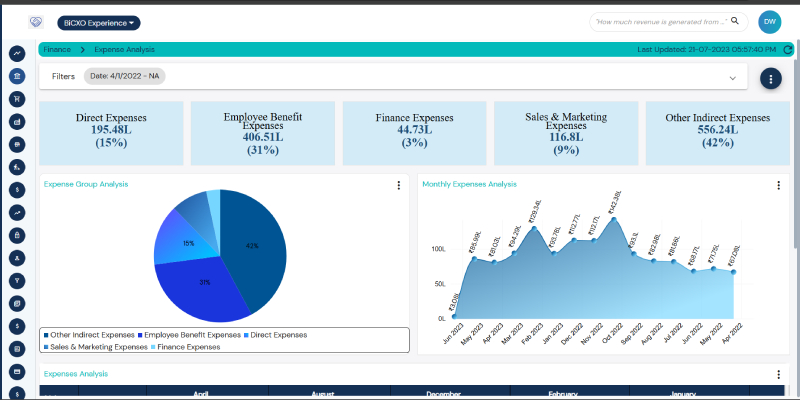
Table of contents:
- What is Expense Data Analysis?
- Why is an expense data analysis performed?
- Why expense data analysis is important?
- Methods for Expense Data Analysis
- Industry-Wise Expense Analysis
- Conclusion
Why is an expense data analysis performed?
Financial performance can be understood through expense data analysis. It aids in locating budget inefficiencies. It guarantees the efficient use of monetary resources. Initiatives to reduce costs are supported by expense data analysis. Expense data analysis increases profitability through cost control. It facilitates adherence to financial regulations. It aids in predicting and strategic planning. Expense data analysis is done by businesses to prevent financial mismanagement and excessive spending. Cash flow management is supported by routine spending analysis. In order to ensure alignment with financial objectives, businesses can also use expense data analysis to compare actual spending with anticipated budgets.
Why expense data analysis is important?
Transparency in financial management is ensured via expense data analysis. It helps to find areas where money can be saved. It stops financial mismanagement and excessive spending. Expense data analysis promotes the sustainability of businesses. It increases the accuracy of financial reporting. It offers a foundation for well-informed choices. Expense data analysis aids in the identification of financial anomalies and fraud. It guarantees adherence to budgetary objectives. Regular expense data analysis helps organizations to manage their operating expenses in a better way. It helps determine the return on investment for different costs. Businesses can increase efficiency and optimize resources by knowing where money is spent.
Methods for expense data analysis
- Classification of Expenses: There are three types of expenses which are fixed, variable and discretionary. Fixed costs don’t change. Activity determines how much is spent on variable costs. Discretionary expenses are those that are not absolutely necessary. Businesses might find possibilities for cost reduction by classifying expenses. Organizations can more effectively allocate resources when they have a better understanding of the types of expenses.
- Analysis of Trends: A given time period’s worth of historical spending data is examined. Spending trends and patterns are found. Past data is used to anticipate future expenses. Trend analysis is used by businesses to predict their future financial requirements. By recognizing patterns in spending, businesses can take proactive steps to reduce costs.
- Variance Analysis: Budgeted and actual spending are contrasted. In order to comprehend cost variances, differences are examined. Variance analysis identifies places where money is being spent too much or too little. Variance analysis is used by organizations to increase the accuracy of their budgets. It facilitates the detection of unforeseen financial shifts and the implementation of remedial measures.
- Ratio Analysis: To evaluate the efficiency of expenses, financial ratios are employed. The ratio of expenses to revenue aids in comprehending cost structure. Financial performance is indicated by the operating expense ratio. Ratio analysis sheds light on the efficacy of cost control. Financial ratios are used by businesses to compare their spending to industry norms.
- Benchmarking: Costs are contrasted with industry norms. Cost effectiveness is compared to rivals. Cost management best practices are noted. Organizations can better understand how their costs stack up against those of similar businesses by using benchmarking. It makes it possible for decision-makers to implement cost-cutting measures that boost competitiveness.
- Breakeven Point Analysis: It looks at how costs, revenue and profitability relate to one other. They figure out the break-even point. It supports cost-control and pricing initiatives. Businesses base their pricing decisions on break-even research. Setting financial goals and reducing risks are made easier with an understanding of the break-even point.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Inflows and outflows of cash are tracked. The state of liquidity is evaluated. There is guaranteed to be efficient cash management. Businesses can preserve their financial stability by using cash flow analysis. Keeping an eye on cash flow guarantees that businesses have the money to pay their debts.
- Activity-based costing (ABC): Expenses are distributed according to business operations. Financial decision-making is enhanced by accurate cost assignment. Operational inefficiencies are found. ABC facilitates more efficient resource allocation for organizations. Increased operational efficiency results from an understanding of activity-based expenses.
Effective expense data analysis empowers businesses to make informed financial decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance cost control. By leveraging these methods, organizations can achieve greater financial stability and strategic growth.
Industry-wise expense analysis
- The Retail Industry: Marketing, utilities, rent and inventory are major costs. Analysis of inventory turnover is essential. Costs of inventories and sales are regularly tracked. In order to increase profitability, retail organizations concentrate on controlling inventory expenses. Analysing marketing-related costs aids in improving promotional tactics.
- The Manufacturing Industry: Raw materials, labour, equipment upkeep and logistics are important costs. Analysis is done on the cost of goods sold (COGS). Efficiency is achieved by optimizing production costs. Expense analysis is used by manufacturing companies to enhance supply chain management. Profitability is increased when cost-saving measures are found in production operations.
- The Healthcare Industry: Medical supplies, personnel, equipment and compliance fees are all significant expenses. Costs of patient treatment are examined. Financial performance is impacted by insurance and regulatory costs. Expense analysis is used by healthcare companies to better allocate resources. Financial stability is ensured by controlling health care expenses.
- The Technology Industry: Software licenses, cloud services and research & development are the major cost components. The costs of IT infrastructure are evaluated. Benefits and pay for employees are examined. Expense analysis is a tool used by technology companies to control operating costs. Optimizing software development and infrastructure investments requires an understanding of IT expenses.
- The Hospitality Industry: Labor, food and beverage charges and facility upkeep are the key costs. There is a cost-per-room analysis. Variations in seasonal expenses are tracked. Businesses in the hospitality industry examine the expenses associated with guest services. Profitability increases when food and beverage costs are controlled.
- The Financial Services Industry: Marketing, IT systems, risk management and compliance are all included in operational costs. The costs of regulations are examined. The costs of acquiring and keeping customers are assessed. Expense data analysis is a tool used by financial organizations to guarantee regulatory compliance. Enhancing service efficiency requires an understanding of operating expenses.
- The Logistics and Transportation Industry: Fuel, labour and fleet maintenance are important cost factors. Cost reduction is aided by route optimization. The costs of freight and warehousing are examined. Expense data analysis is used by transportation companies to increase operational effectiveness. Profitability is increased by controlling fuel costs.
- The Construction Industry: Project management, labour, equipment and raw materials are major costs. Budget conformance is ensured by cost estimation. The costs of contractors and suppliers are tracked. In order to guarantee project profitability, construction companies examine costs. Cost efficiency is increased by controlling supplier costs.
- The Education Industry: Student services, infrastructure, technology and faculty salaries are the main costs. Tuition prices are influenced by operational expenses. The amount allotted to academic resources is examined. Universities and schools examine spending in order to maximize their financial resources. Controlling educational costs guarantees sustainability and affordability.
- The Telecom Industry: Network infrastructure, customer service and licensing are among the major expenses. Cost structure is impacted by technology investment. Expense management and revenue generation are related. Expense data analysis is used by telecom companies to control infrastructure and operating costs. Financial sustainability is ensured by knowing costs.
To conclude, Financial planning and cost control are based on expense data analysis. Effective cost control is essential to the sustainability and profitability of a business. Alignment with financial objectives is ensured by routine analysis. Organizations that do extensive expense data analysis obtain a competitive advantage. Expense insights are used by businesses to inform strategic choices. Effective cost management techniques are essential for financial success.